Measurement
Measurement:- Measurement is defined as the process of comparison of an unknown quantity with a known or standard quantity.
In ancient times there are no standard measurements like inches, centimetres, grams, feet etc.
In that time hey used cubits, spans etc. One person's cubit or span is different from others. Sometimes the quarrels also happened.
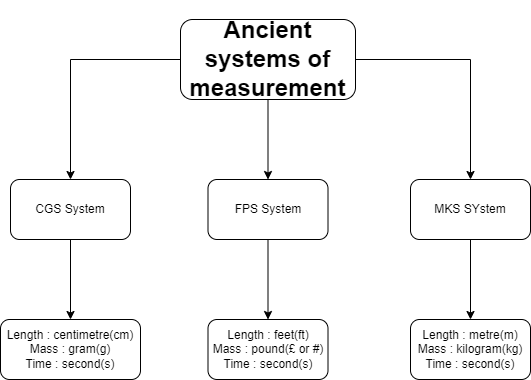
So some people discussed and invented three different systems of measurement. They are CGS System, FPS System and MKS Systems.
Ancient systems of measurement with units
Measuremnt
CGS
FPS
MKS
Length
centimetre(cm)
foot(ft)
metre(m)
Mass
gram(g)
pound(#)
kilogram(kg)
Time
second(s)
second(s)
second(s)
Mindmapping
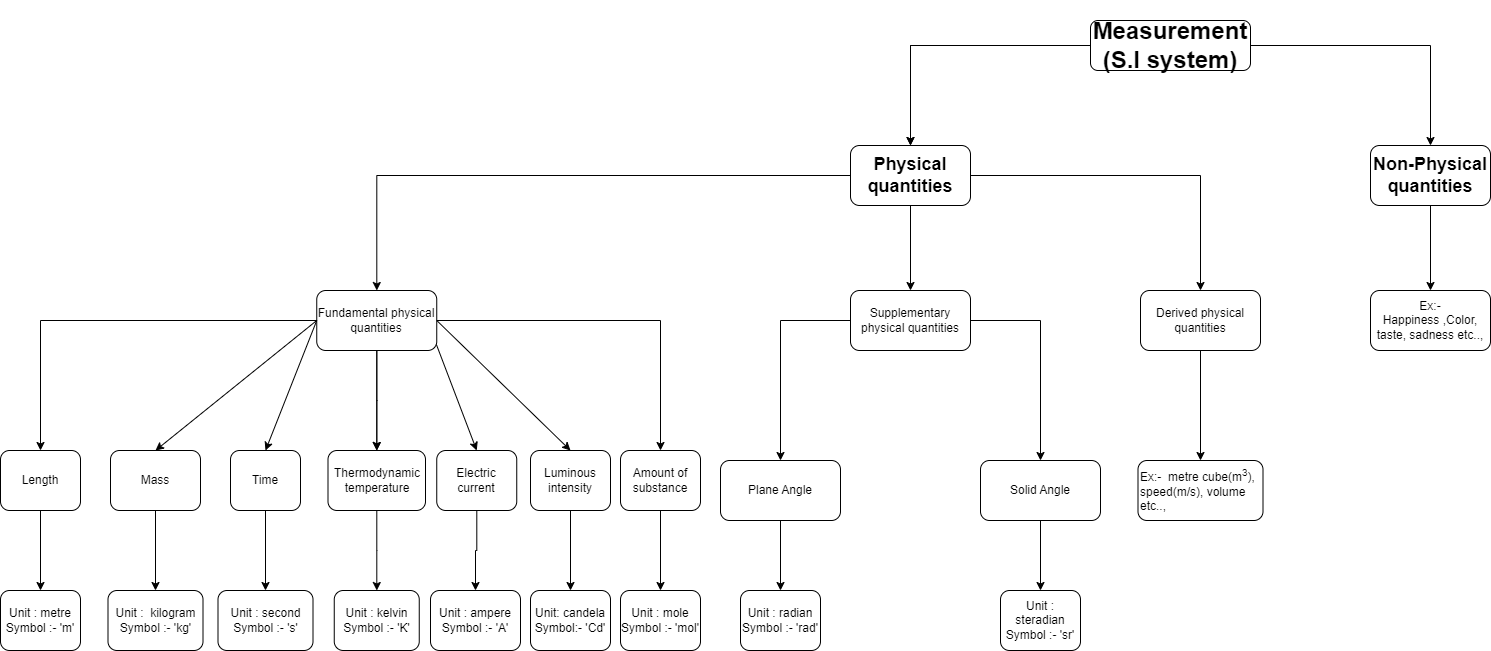
With these systems also some problems came. In one place one person used one system. In another place other system was used. With that when people of one place shifted to another place they don't know that measurement. So they used their place system only. The measuremnet is different now. So the quarrel came with these systems also. So they again discussed and invented one common system that is known as S.I system(Standard International system).
S.I system
Fundamental physical quantities with units
Fundamental physical quantity
Unit
Symbol
Length
metre
m
Mass
kilogram
kg
Time
second
s
Thermodynamic temperature
kelvin
K
Electric current
ampere
A
Luminous Intensity
candela
Cd
Amount of substance
mole
mol
Supplementary physical quanitites:- Supplementary physical quantity is a physical quantity that is used for calculation (on a secondary level). Plane angle and solid angle are two supplementary units of two purely" geometrical physical quantities.
Supplementary physical quantities with units
Supplementary physical quantity
Unit
Symbol
Plane angle
radian
rad
Solid angle
steradian
sr
Derived physical quantities:- Quantitites which depend on other physical quantities are called derived physical quantities.
Examples:- Speed, Velocity, Density,Area, Volume etc.
Mindmapping
Fundamental units:- Units of fundamental physical quantities are called fundamental physical quantities.
Examples:- kilogram, ampere, second, metre etc.
Derived units:- Units of derived physical quantities are called derived physical quantities.
Examples:- m2, m3 etc.
Multiples and submultiples of units
Multiples:- Units used to measure larger quantities are caled multiples.
Submultiples:- Units used to measure smaller quantities are caled submultiples.
Example:- We can't use metre for all purposes. When we measuring distance from India to USA we can't understand in metres. So we use kilometers and when we are measuring thickness of a pencil metre is not sufficient. So we use millimetres.In these cases kilo is a multiple of metre and milli is submultiple of same unit metre.
Some important prefixes for units in S.I System
Prefix
Multiple
Symbol
Deca
101
da
Kilo
1000 = 103
kg
Mega
1000000 = 106
M
Giga
1000000000 = 109
G
Tera
1000000000000 = 1012
T
Prefix
Submultiple
Symbol
Deci
1/10th = 10-1
d
Centi
1/100th = 10-2
c
Milli
1/1000th = 10-3
m
Micro
1/1000000th = 10-6
Greek letter mu
Nano
1/1000000000th = 10-9
n
Pico
1/1000000000000th = 10-12
p
Rules for writing S.I Units
- The symbols used for units are always written in lowercase.
S.No
Quantity
Correct
Wrong
1
Mass
kg
Kg
2
Length
m
M
3
Time
s
S
- Name of the unit should start with lowercase letter even if it is named after a scientist.
S.No
Quantity
Correct
Wrong
1
Force
newton
Newton
2
Temperature
kelvin
Kelvin
3
Energy
joule
Joule
- Symbol of unit name after a scientist, should start with with an uppercase letter.
S.No
Quantity
Correct
Wrong
1
Force
N
n
2
Temperature
K
k
3
Energy
J
j
| Measuremnt | CGS | FPS | MKS |
|---|---|---|---|
| Length | centimetre(cm) | foot(ft) | metre(m) |
| Mass | gram(g) | pound(#) | kilogram(kg) |
| Time | second(s) | second(s) | second(s) |

S.I system
| Fundamental physical quantity | Unit | Symbol |
|---|---|---|
| Length | metre | m |
| Mass | kilogram | kg |
| Time | second | s |
| Thermodynamic temperature | kelvin | K |
| Electric current | ampere | A |
| Luminous Intensity | candela | Cd |
| Amount of substance | mole | mol |
| Supplementary physical quantity | Unit | Symbol |
|---|---|---|
| Plane angle | radian | rad |
| Solid angle | steradian | sr |
Some important prefixes for units in S.I System
| Prefix | Multiple | Symbol |
|---|---|---|
| Deca | 101 | da |
| Kilo | 1000 = 103 | kg |
| Mega | 1000000 = 106 | M |
| Giga | 1000000000 = 109 | G |
| Tera | 1000000000000 = 1012 | T |
| Prefix | Submultiple | Symbol |
|---|---|---|
| Deci | 1/10th = 10-1 | d |
| Centi | 1/100th = 10-2 | c |
| Milli | 1/1000th = 10-3 | m |
| Micro | 1/1000000th = 10-6 | Greek letter mu |
| Nano | 1/1000000000th = 10-9 | n |
| Pico | 1/1000000000000th = 10-12 | p |
| S.No | Quantity | Correct | Wrong |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Mass | kg | Kg |
| 2 | Length | m | M |
| 3 | Time | s | S |
| S.No | Quantity | Correct | Wrong |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Force | newton | Newton |
| 2 | Temperature | kelvin | Kelvin |
| 3 | Energy | joule | Joule |
| S.No | Quantity | Correct | Wrong |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Force | N | n |
| 2 | Temperature | K | k |
| 3 | Energy | J | j |